

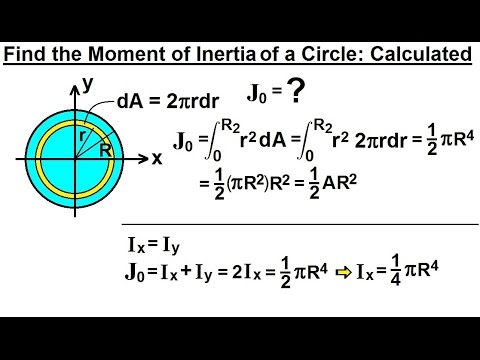
In this regard, what is the moment of inertia of a uniform circular disk? Likewise, what does radius of gyration mean? Radius of gyration or gyradius of a body about an axis of rotation is defined as the radial distance of a point, from the axis of rotation at which, if whole mass of the body is assumed to be concentrated, its moment of inertia about the given axis would be the same as with its actual distribution of mass. The polar moment of inertia, also known as second polar moment of area, is a quantity used to describe resistance to torsional deformation (deflection), in cylindrical objects (or segments of cylindrical object) with an invariant cross-section and no significant warping or out-of-plane deformation. Keeping this in view, what is polar moment of inertia of circle? This equation is equivalent to I = π D 2 / 64 when we express it taking the diameter (D) of the circle. Here, r is the radius and the axis is passing through the centre. What will be the the radius of gyration of a circular plate of diameter 10cm?Ĭlarification: The moment of inertia of a circle, I = πD 4/64 = 491.Moment of inertia of a circle or the second- moment area of a circle is usually determined using the following expression I = π R 4 / 4. What is the unit of radius of gyration?Ĭlarification: The radius of gyration = (length 4/length 2)1/2 = lengthĨ.

of the plane area be represented by IG, then the moment of the inertia of the given plane area about a parallel axis AB in the plane of area at a distance h from the C.G. What is the formula of theorem of parallel axis?Ĭlarification: The theorem of parallel axis states that if the moment of inertia of a plane area about an axis in the plane of area theough the C.G. What is the formula of theorem of perpendicular axis?Ĭlarification: Theorem of perpendicular axis stares that if I XX and I YY be the moment of inertia of a plane section about two mutually perpendicular axis X-X and Y-Y in the plane of the section then the moment of inertia of the section I ZZ about the axis Z-Z, perpendicular to the plane and passing through the intersection of X-X and Y-Y is given by the formulaĦ. The formula of radius of gyration is given as k 2 = I/A.ĥ. What is the formula of radius of gyration?Ĭlarification: The radius of gyration of a body about an axis is a distance such that its square multiplied by the area gives moment of inertia of the area about the given axis. M = mass, a = area, l = length, r = distance.Ĥ. The definition of the centroid of volume is written in terms of ratios of integrals over the volume of the body.Ĭlarification: The formula of the moment of inertia is, MOI = ar 2 where If the density is uniform throughout the body, then the center of mass and center of gravity correspond to the centroid of volume.

Point, where the total volume of the body is assumed to be concentrated is _Ĭlarification: The centroid of the volume is the point where total volume is assumed to be concentrated. Most of the times it is either the standard x or y axis or the centeroidal axis.Ģ. The axis about which moment of area is taken is known as _Ĭlarification: The axis of reference is the axis about which moment of area is taken. This set of Strength of Materials Multiple Choice Questions on “Moment of Inertia”.ġ.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
